- 0086-373-2688227
- sales@hmbattery.com

Standard voltage:
1.2VCharging current:
0.2C5A1). Good performance of discharge
2). Strong resistance to overcharge/over discharge
3). Good flame retardancy
4). Large range of working temperature
5). High safety performance
Application:
1).UPS
2).Power Plants
3).Electrical power system
Nominal Voltage | 1.2V | |
Capacity(5HR,20℃) | 200Ah | |
Dimension | Length | 167mm |
Width | 162mm | |
Total Height | 345mm | |
Approx. Weight | 13.5Kg | |
Internal resistance (Fully charged, 20℃ ) | 0.75*10-3Ω | |
Capacity affected by temperature (5HR) | 20℃ | ≥100% |
-18℃ | ≥80% | |
Self-discharge (20℃) | 28 days | <25% |
Nominal operating temperature | 20℃±5℃ | |
Operating temperature range | –20℃~45℃ | |
Float charge voltage(20℃) | 1.40~1.42V/cell | |
Boost charge voltage | 1.54~1.69V/cell | |
Standard charging current | 40A | |
Terminal material | Nickel- Clad Steel | |
◆According to IEC cycle time is more than 500,
float charging life is more than 15 years.
◆PP flame retardant container.
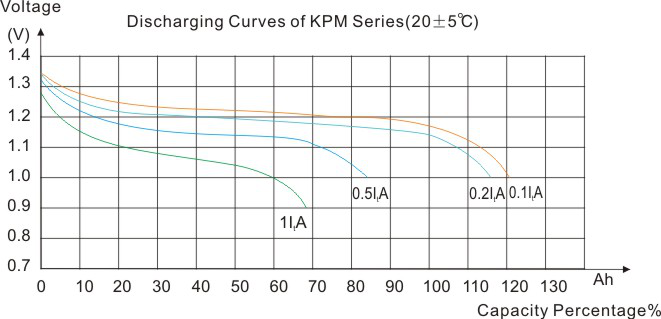
Discharging Characteristics
Constant Current Discharge Characteristics (A, 20℃)
F.V/TIME | 1min | 5min | 10min | 15min | 1h | 2h | 3h | 5h | 8h |
1.0V | 480 | 360 | 312 | 270 | 150 | 92 | 64 | 40 | 25.2 |
1.05V | 400 | 320 | 264 | 240 | 140 | 84 | 62 | 39.2 | 24.8 |
1.10V | 360 | 260 | 220 | 200 | 120 | 76 | 60 | 38.8 | 24.4 |
1.14V | 260 | 190 | 160 | 140 | 90 | 66 | 54 | 36 | 23.6 |
Table 6 Troubles and trouble shootings
Troubles | Causes | Trouble shootings |
The capacity of the battery decreases | 1.The electrolyte has been used for a long time and the carbonate content in it is too high. | Replace the electrolyte |
2.The electrolyte is improperly used. | Replace the electrolyte | |
3.The electrolyte isn’t enough, and the level of the electrolyte is below the top of the plates. | See Table 5 | |
4.Hurmful impurities contained in the electrolyte is too high. | Replace the electrolyte | |
5.The charge/discharge method is not correct. | See the 5.2 and 6 | |
6.Short-circuit or slight-short circuit in the cell | Replace the short-circuit cell. | |
7.Short-circuit or slight-short circuit occurs out of the cell. | Keep the cells in a dry temperature | |
8.The instruments used is not correct. | Check and rectify the ampere meter and voltmeter. | |
Voltage is not normal | 1.The inner circuit of the cell is short or cut, the electrolyte has been run out. | Clean the cell, or change the electrolyte |
2.The out circuit of the battery is short or cut. | Keep the cell dry, and check | |
3.Contact fault | Check and repair | |
Bubbles appear in the inside of the cell | The electrolyte contains organic impurities | Replace the electrolyte |
The cell container swells | 1.The positive plate swells. | If necessary, change the cell. |
2.The vent is blocked up. | Clean with hot water or replace it. | |
Creeping of electrolyte | 1.The level of electrolyte is too high | Drain out the superfluous electrolyte. |
2.The vent plug and terminal is unsealed | Replace the sealing parts and screw tightly. | |
3.Too much electrolyte overflows. | Clean and keep dry |
Product Picture
